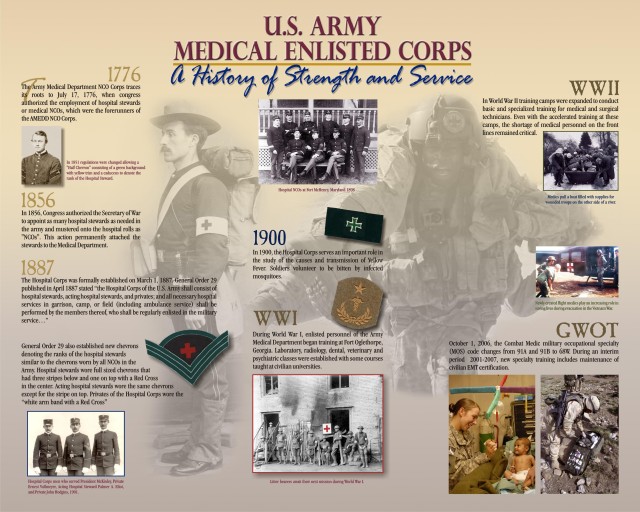
FORT SAM HOUSTON, Texas (March 1, 2012) -- Though the Medical Enlisted Corps was formally established as the Hospital Corps on March 1, 1887, their history dates back to the Revolutionary War.
At the outbreak of the war, medical support was hampered not only by the limited availability of trained medical personnel, but the lack of adequate medicine and equipment.
Insufficient care of the wounded and the lack of treatment and prevention of the diseases that ravaged the Army caused George Washington to address the issue of medical care with Congress.
Finally, on July 27, 1775, Congress authorized the establishment of a Medical Service. This date is known as the Anniversary of the Army Medical Department, or AMEDD. This important step made provisions for a Director General and Chief Physician (Surgeon General), four surgeons, one apothecary, 20 surgeon's mates, one clerk and two storekeepers. It also provided one nurse to every 10 sick, and laborers as needed.
Dr. Benjamin Church was selected as the first surgeon general. Based on the recommendations of the director general, on July 17, 1776, Congress authorized the employment of hospital stewards who were the forerunners of the AMEDD Noncommissioned Officer Corps.
General Order 29, published in April of 1887, assigned enlisted members to the corps and permanently attached them to the Medical Department.
After one year of service with Hospital Corps, privates were eligible for appointment as acting hospital stewards. After one year of probation and passing of another examination, they could be appointed "permanent" hospital stewards.
In its first year, some 600 privates transferred to the new corps, with only 24 passing their examinations and promoted to acting hospital stewards.
On March 2, 1903, the Hospital Corps was disestablished. The terms hospital steward and privates of hospital corps were replaced by the terms sergeant and private with an exception for the master hospital sergeant which was used until 1920.
Today, there are more than 36,000 enlisted serving in Army Medicine.

Social Sharing