Army Materiel Command (AMC) has been proactively engaged in implementing Zero Trust cybersecurity initiatives, aligning with the broader federal government's push towards this advanced security model.
From June 2023 through May 2024, AMC led a significant effort to address Zero Trust policy impacts on Military Intelligence/Intelligence, Surveillance & Reconnaissance (MI/ISR) Systems Readiness and Facilities.
Katherine Coviello, AMC's Special Advisor for Enterprise Intelligence and Security, spearheaded an Army-wide Operational Planning Team (OPT) focused on this initiative. The OPT brought together experts from various Army components to shape cybersecurity requirements for the MI/ISR portfolio, ensuring alignment with both Army and Intelligence Community implementation plans for Zero Trust.
“Policy always lags behind technology,” Coviello noted, emphasizing the need for proactive measures. “So when one of our mission partners in (U.S. Army Forces Command) G-2 highlighted this emerging framework, we understood that we needed to move out smartly to inform the requirements process and bake in security design as early as possible to drive success, cyber-hardening and system readiness.”
This team, described as a “coalition of the willing,” worked to ensure compliance and integration with Zero Trust principles across Army systems.
AMC's proactive approach in addressing Zero Trust requirements early in the process aims to inform the requirements process, incorporate security design from the outset, enhance cyber-hardening measures and improve overall system readiness.
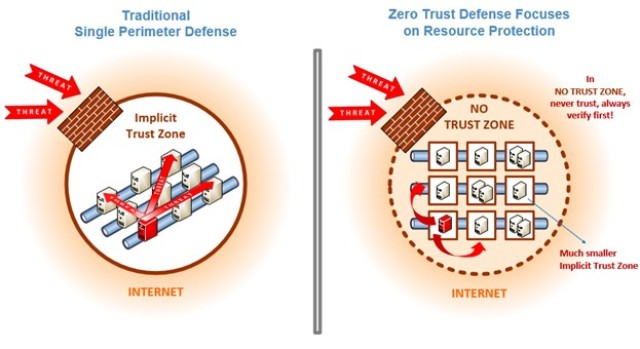
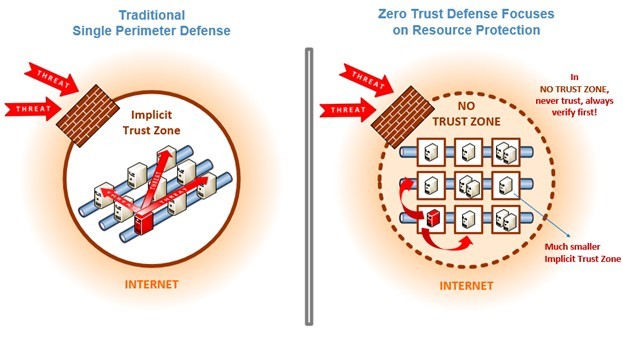
This strategy aligns with the Zero Trust philosophy of “never trust, always verify,” which is gaining traction across federal agencies. The approach is particularly relevant in today's distributed work environments and multi-cloud infrastructures, providing robust security controls for connections between users, devices, applications, and data.
AMC's efforts are part of a larger government-wide initiative to implement Zero Trust architecture. The federal government has taken several steps in this direction, including:
• The release of the Zero Trust Strategy by the Department of Defense in November 2022;
• The establishment of the Zero Trust and Software-Defined Networking Steering Group by federal IT officers in February 2018;
• The release of Special Publication 800-207 by NIST in August 2020, offering guidance on zero trust architecture adoption.
These initiatives reflect the growing recognition that traditional network security models are increasingly inadequate in the face of evolving cyber threats. The Zero Trust model, with its emphasis on continuous verification, granular access control, and least privilege access, offers a more comprehensive approach to cybersecurity.
By taking a leading role in implementing Zero Trust principles, AMC is positioning itself at the forefront of military cybersecurity efforts, helping to strengthen the Army's overall security posture in an increasingly complex digital landscape.
Social Sharing