The Big Picture
Weekly company training meetings are vitally important to developing unit training proficiency. They ensure past training is reviewed for effectiveness, provide a forum to discuss and coordinate future training, and for the commander to consider feedback and to provide training guidance to subordinate company leaders. FM 7-0 is a leader’s primary reference for understanding the importance of company training meetings.
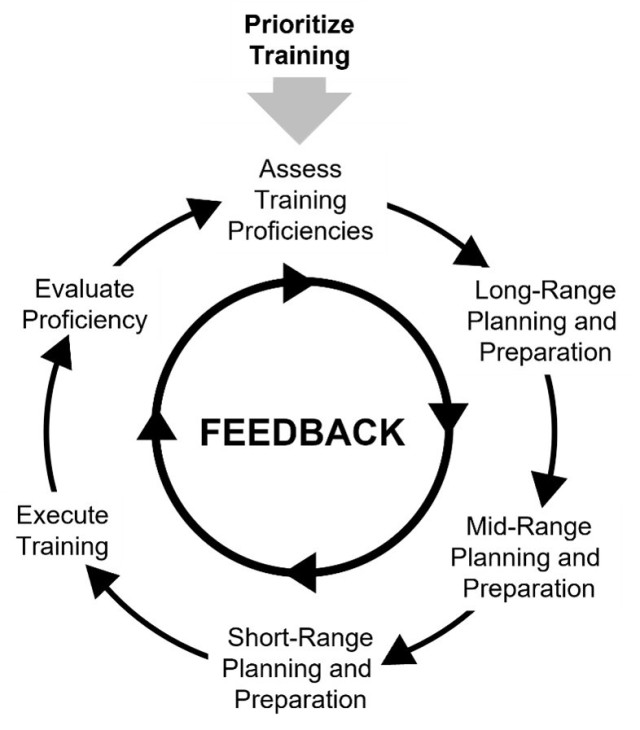
Company training meetings are particularly important during the short-range planning horizon when training event execution is imminent: these meetings are only a part of the bigger picture of the Training Management Cycle.
Training Management Cycle
The Training Management Cycle provides all Army leaders a logical, chronological framework for developing unit training proficiencies (mission-essential tasks, weapons qualification, collective live-fire). Company training meetings occur weekly throughout the training management cycle, ensuring at the lowest echelons training is executed, evaluated and company commanders assess the results.
Prioritize and Assess Training Proficiencies. The first step in the cycle requires the commander, based on the unit mission, to prioritize and assess each of the unit’s three training proficiencies. Once the commander prioritizes training, planning and preparation can begin.
Long-Range Planning and Preparation. The commander begins developing a long-range training plan to determine who, what, when, where and why the unit will train in the next fiscal year (FY). This process results in the timely publication of the unit’s Annual Training Guidance (ATG). Publication of ATG is critical and ensures every echelon plans and identifies training resources early in the cycle. See FM 7-0, tables 3-1 and table 3-2 for specific ATG publication dates by echelon.
Mid-Range Planning and Preparation. As the unit executes ATG during the FY, mid-range planning and preparation centers on periodic (semi-annual and quarterly) reviews of training conducted and guidance refinement as necessary. Semi-annual and quarterly training briefings (SATB/QTB) provide senior commanders the status of ATG compliance as the FY progresses. Training meetings held at brigade and battalion level also track ATG progress to ensure training resources for subordinate companies are coordinated and available when training begins.
Short-range Planning and Preparation. Throughout the FY, company level units conduct weekly training meetings as a primary part of their training battle rhythm. Through these meetings, units continuously monitor and manage training in the short-range planning horizon (Weeks T-6 to T). This period just before training event execution is the culmination of long-, mid-and short-range planning and preparation. It is in this period of the Training Management Cycle that final training event preparations are made, final resource coordination is made, resources received, and rehearsals held. It is also at T-6 that company training schedules are approved and published.
Conducting Company Training Meetings
Company training meetings are the center of gravity of unit training management. During these weekly meetings, company leaders synchronize and coordinate their training efforts in support of the commander’s ATG. Training and only training is discussed to maintain focus, direction and purpose.
The company commander chairs the training meeting with maximum leader participation (see FM 7-0, Appendix E for a list of attendees and their responsibilities). The Digital Training Management System (DTMS) operator displays current unit training information to facilitate information sharing and minimize the need to reproduce existing data.
Prior to the company training meeting, platoon leaders conduct their own, informal training meeting. The platoon training meeting includes the platoon leader, platoon sergeant and squad leaders. It reviews current platoon training proficiencies, training recently conducted, and future training planning and coordination. It also ensures platoon level training has been recorded using the Small Unit Leader Tool (SULT), which feeds DTMS and updates information for the company meeting.
Company Training Meeting Focus
The commander ensures the agenda is followed and the discussion is concise and to the point. As a minimum, the following topics are the meeting’s focus:
- Current training proficiency overview.
- Training conducted the previous week and a review of subordinate feedback to include:
Leader observations.
After action review (AAR) results.
Completed evaluator training and evaluation outlines.
Other sources of feedback available to the commander.
- Leader development planning focusing on leader development goals and objectives.
- Mid-range planning and preparations (training events inside T-16 to T-7).
- Short-range planning and preparations (training events inside T-6 to T) and the commander’s short-range training guidance.
During the meeting, the crosstalk between leaders ensures actions and lessons learned from previous training are fully discussed, recognized and recorded for future reference.
T-Week Calendars – a Common Point of Reference
During training meetings, ‘T-Week’ is a reference technique unit leaders use in association with each training event (each week of training has its own T-Week reference depending on the week of execution). It counts down the weeks prior to and after each training event – and helps identify the associated actions that need to occur during a particular week. For example, for a company situational training exercise (STX):
T-16 Identify major training facilities (16 weeks before the event)
T-12 Conduct training event planning (12 weeks before the event)
T-11 Refine event requirements (11 weeks before the event), etc.
Leaders develop and modify T-Week calendars based on unit needs in association with installation and command resourcing requirements. For example, coordination for Multiple Integrated Laser Engagement System (MILES) equipment may take 18 weeks to initiate a request on one installation, while on other installations it may take longer. Leaders tailor their T-Week calendars accordingly.
Leveraging Online Training Support
During the meeting, company leaders view current unit training management data, available securely and online through DTMS. Command emphasis on routinely inputting training data into DTMS ensures the information is current, easily accessible and displayable. Using DTMS to display the data precludes the need to create separate products to display training information already recorded and available.
The Army Training Network (ATN) is the primary entry point for all training information and resources. It provides a wealth of training products online to include how-to tutorials, videos and much more. The Combined Arms Training Strategies (CATS) provides recommended training strategies to help develop training plans and identify training resource requirements. The Digital Training Management System (DTMS) provides visibility of training calendars, Mission Essential Task (MET) assessments, access to the Small Unit Leader Tool (SULT) and the Digital Job Book (DJB) and other important training information. Go to https://atn.army.mil to access ATN and all of these resources.
Note: Training and Evaluation Outlines (T&EOs) are easily accessible from each of these systems.
Training Event Planning – 8-Step Training Model
During the company meeting, as the unit discusses future training event planning, leaders refer to the 8-Step Training Model. It is an effective technique for small units (company and below) to plan and prepare individual training events. It is a training management technique to ensure the unit accounts for major actions/activities as training event planning and preparations take place. Leaders are encouraged to refine/modify training models based on unit and installation requirements. The steps of the 8-step training model are:
Conclusion
Company training meetings are the center of gravity of unit training management, ensuring training occurs as planned and is effective. Understanding the ”big picture” of the Training Management Cycle is key to understanding the role and impact company training meetings have in achieving unit training proficiency. These weekly meetings facilitate the vital flow of training information to leaders and provide a primary feedback mechanism for commanders in assessing training effectiveness. To learn more about company training meetings, read FM 7-0 and go to the Army Training Network (ATN) at https://atn.army.mil.



Social Sharing