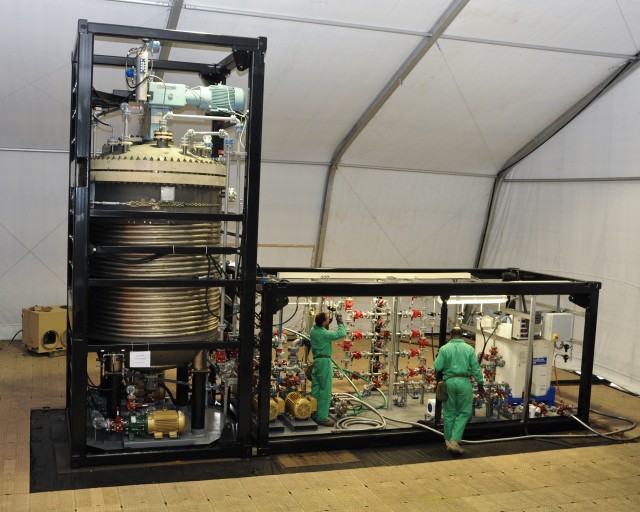
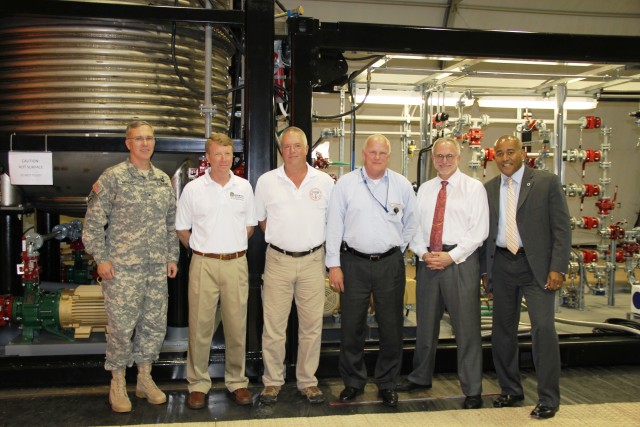
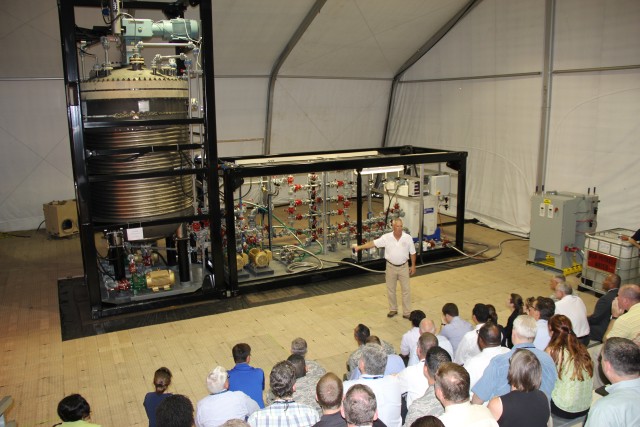
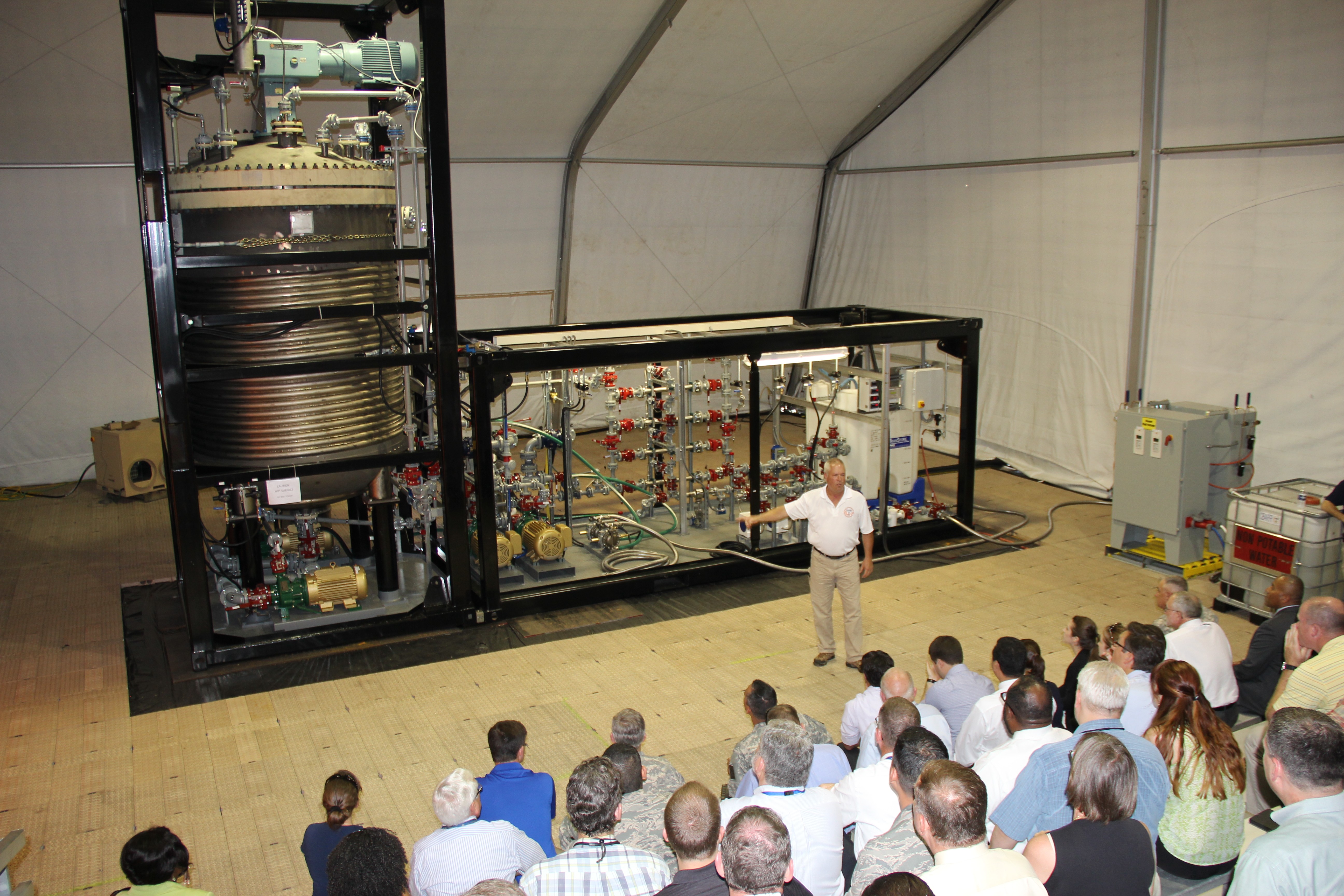
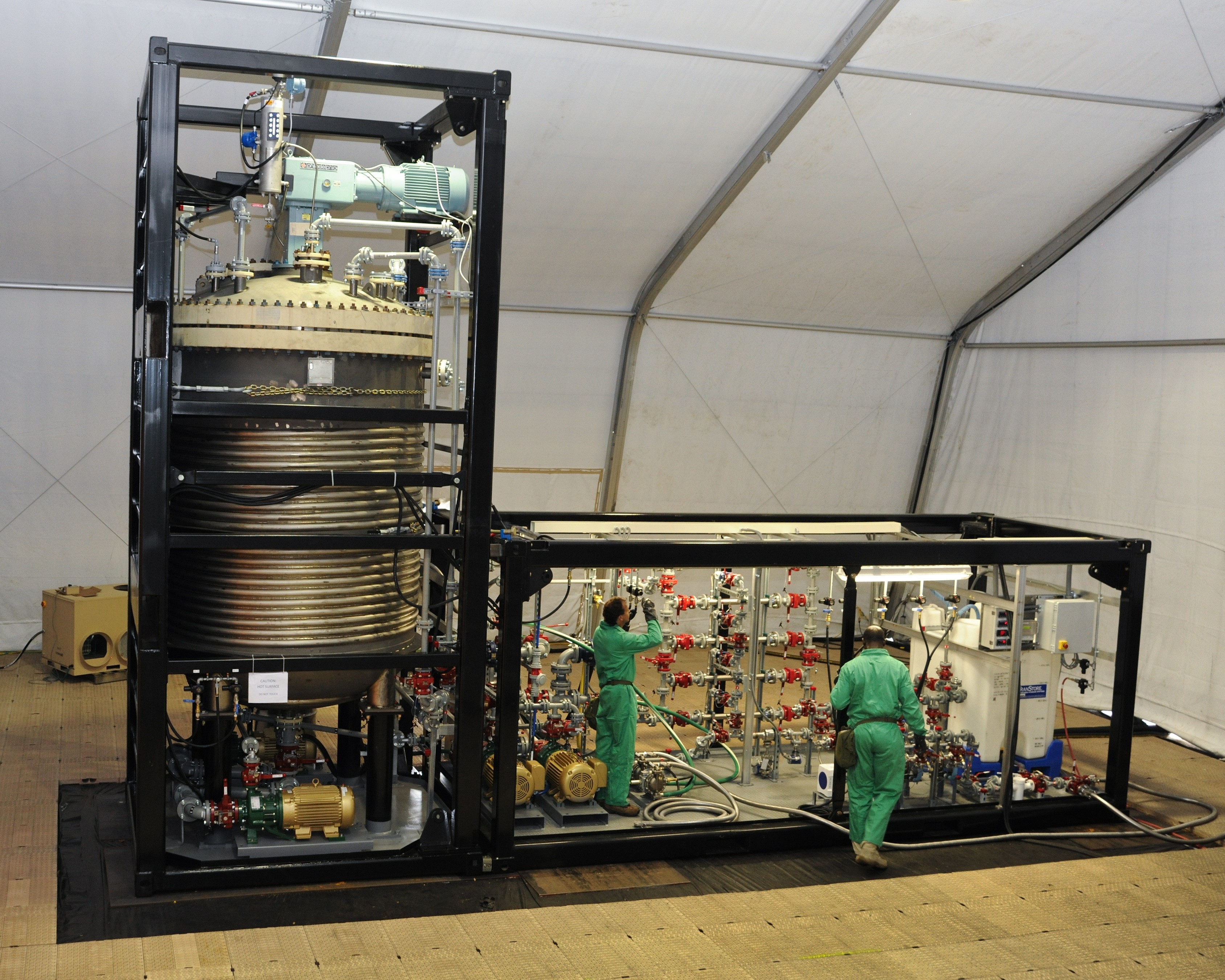
ABERDEEN PROVING GROUND, Md. -- The U.S. Army Edgewood Chemical Biological Center, in partnership with the Defense Threat Reduction Agency, ECBC signed a technology transfer agreement with the Joint Program Executive Office-Chemical Biological Defense on June 27. The official transition took place upon completion of the demonstration of a new transportable, high-throughput neutralization system: the Field Deployable Hydrolysis System.
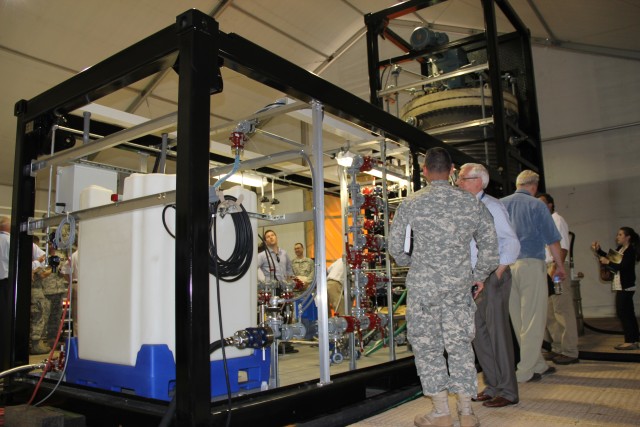
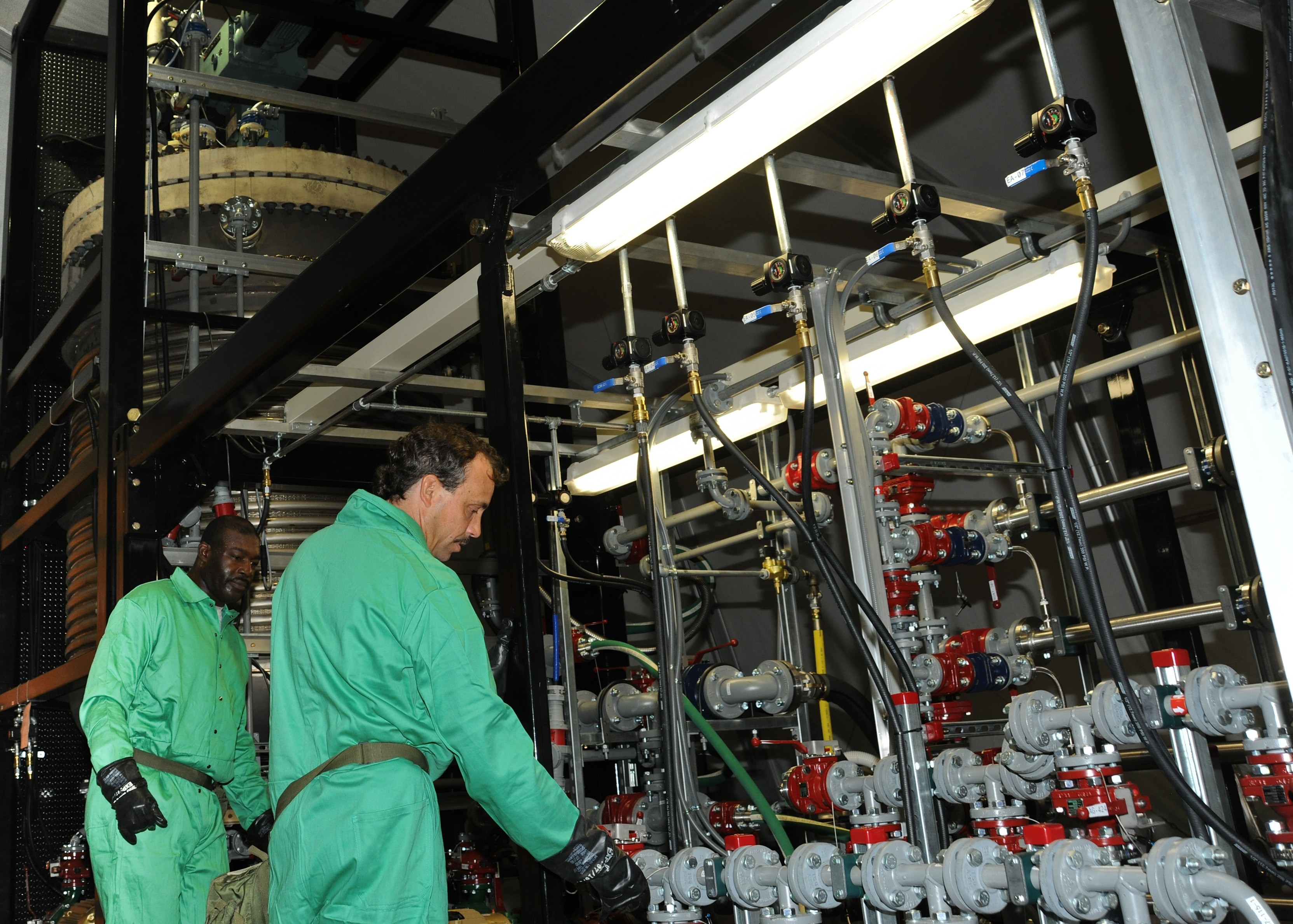
The FDHS helps further the mission of chemical agent disposal operations and is designed to be deployed worldwide, with operational capability anywhere in the world within 10 days of going mobile. The FDHS is designed to change chemical warfare materiel into compounds not useable as weapons. It has the capability to neutralize bulk amounts of known chemical warfare agents and their precursors through chemical reactions involving reagents such as water, sodium hydroxide and sodium hypochlorite. The FDHS uses mixing and heating to facilitate chemical reactions and optimize throughput with a destruction efficiency of 99.9 percent.
"It has been six months to the day since we first conceptualized the design of the FDHS, and now we have a functional working model," said Tim Blades, director of operations for ECBC's Chemical Biological Application and Risk Reduction Business Unit. "The funding from DTRA got us started and with the technical efforts of more than 50 ECBC employees that accounted for 13,000 hours of work, we have now transitioned the project from science and technology to advanced development with the transfer to JPEO-CBD."
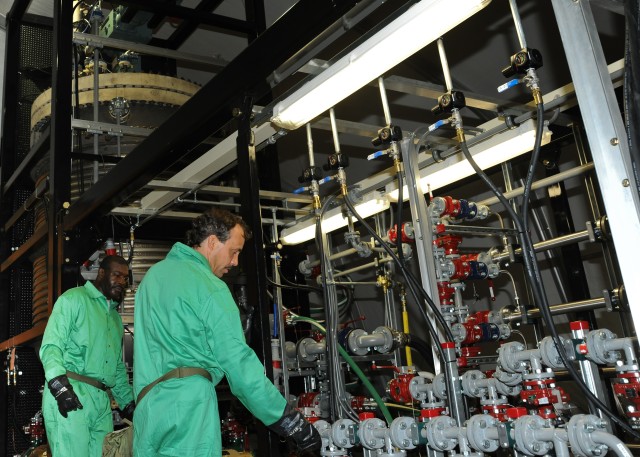
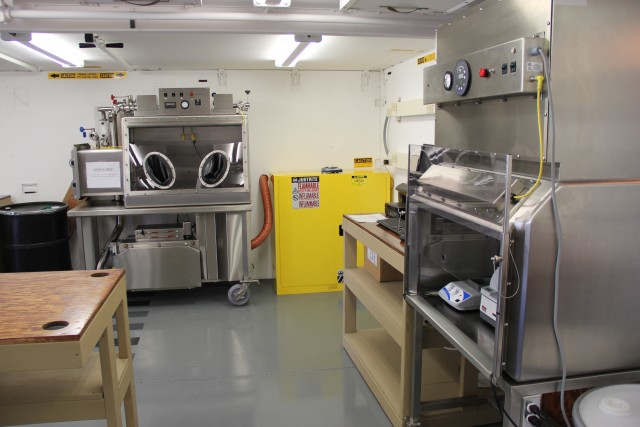
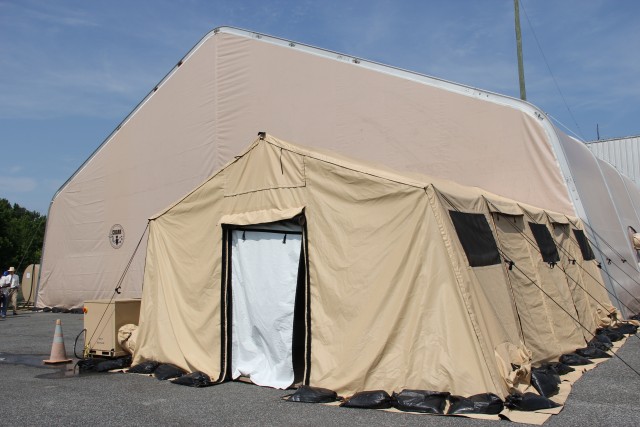
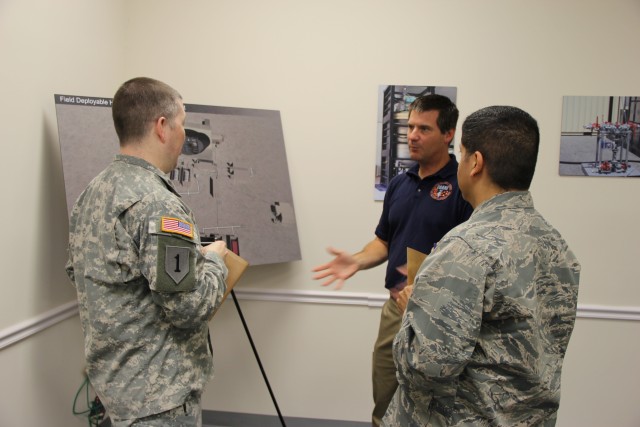
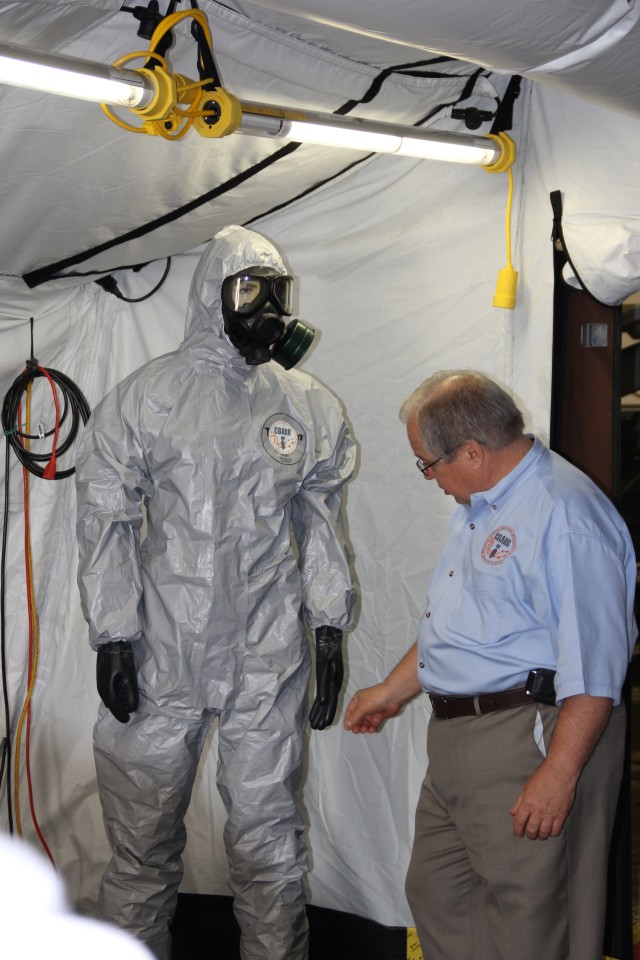
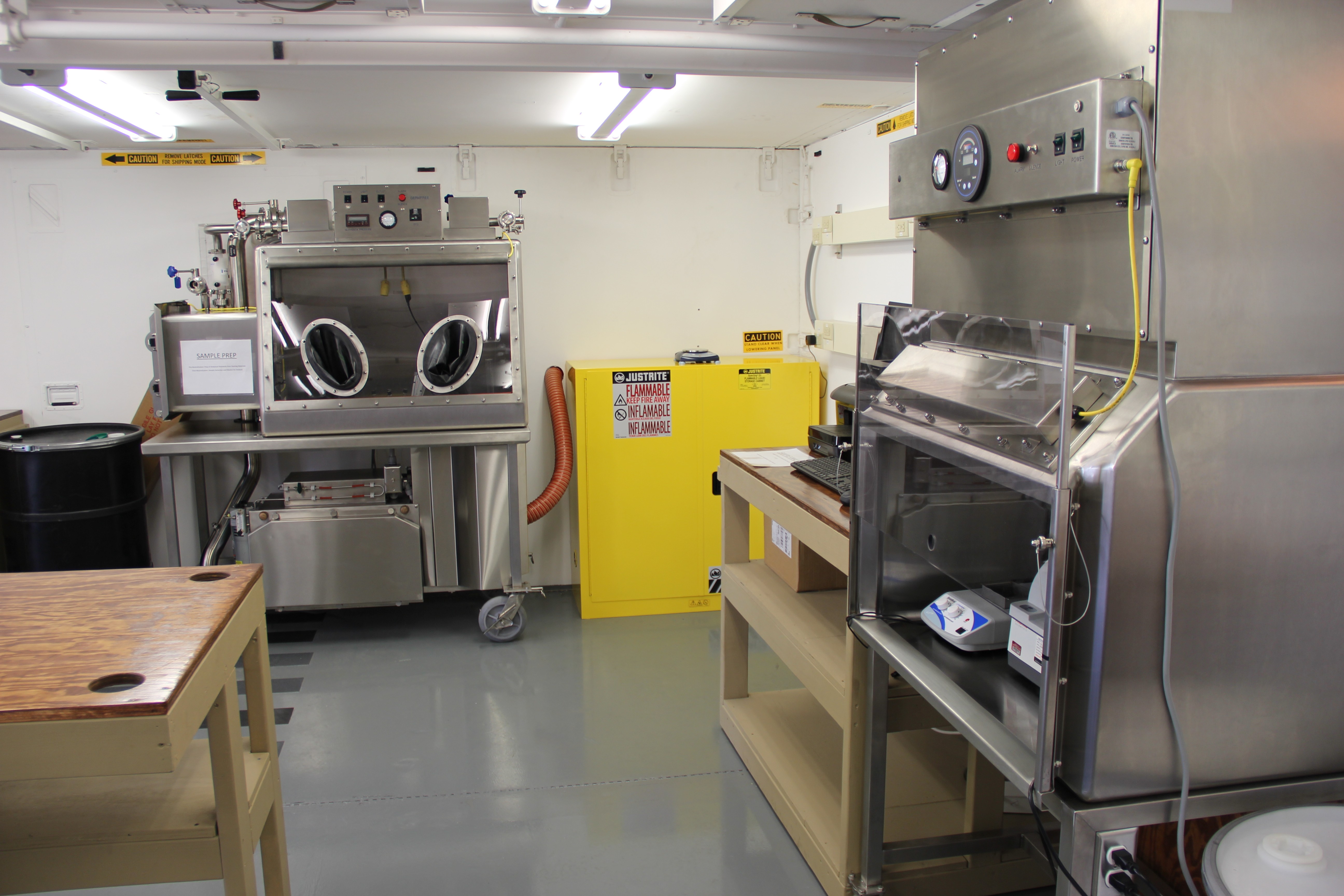
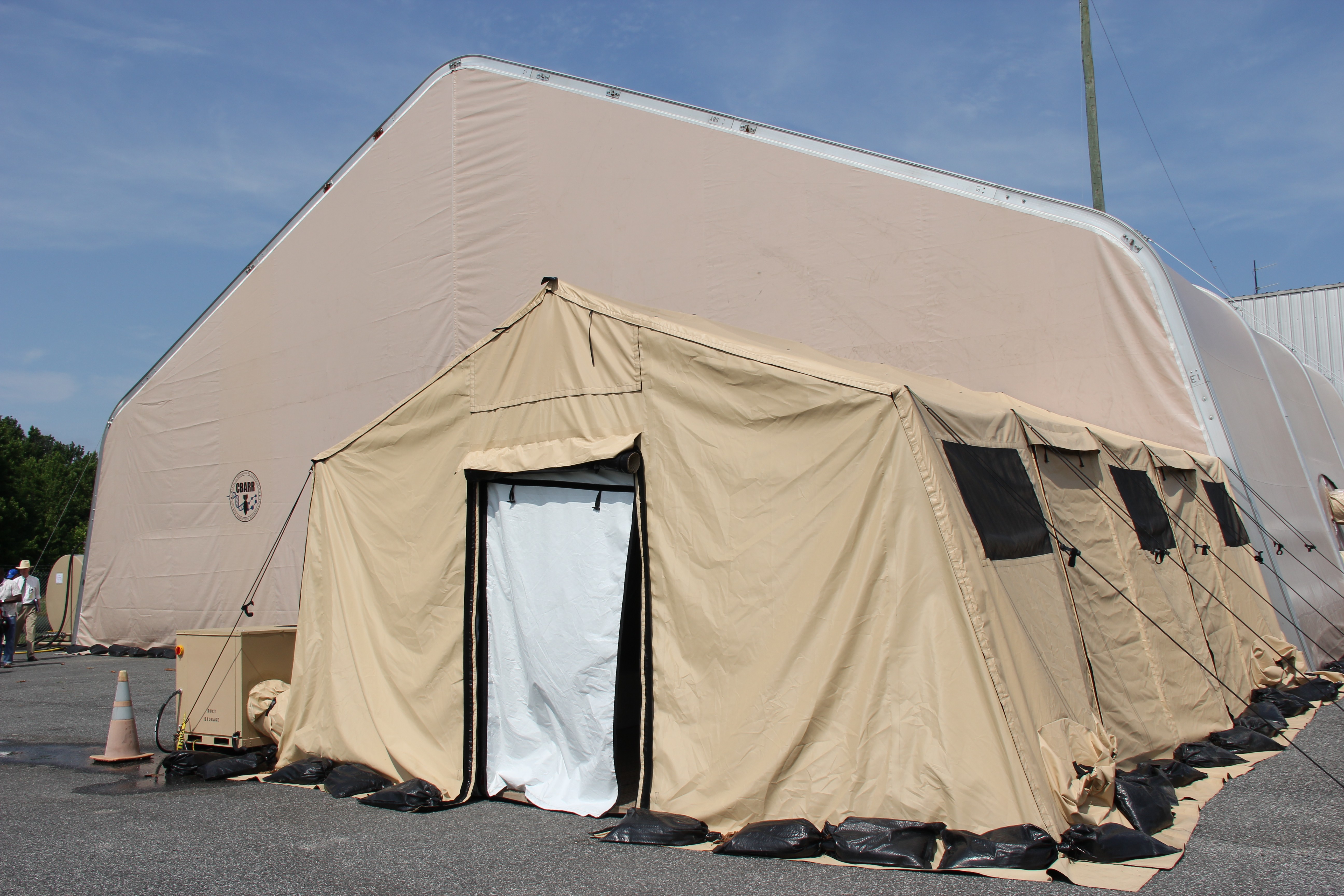
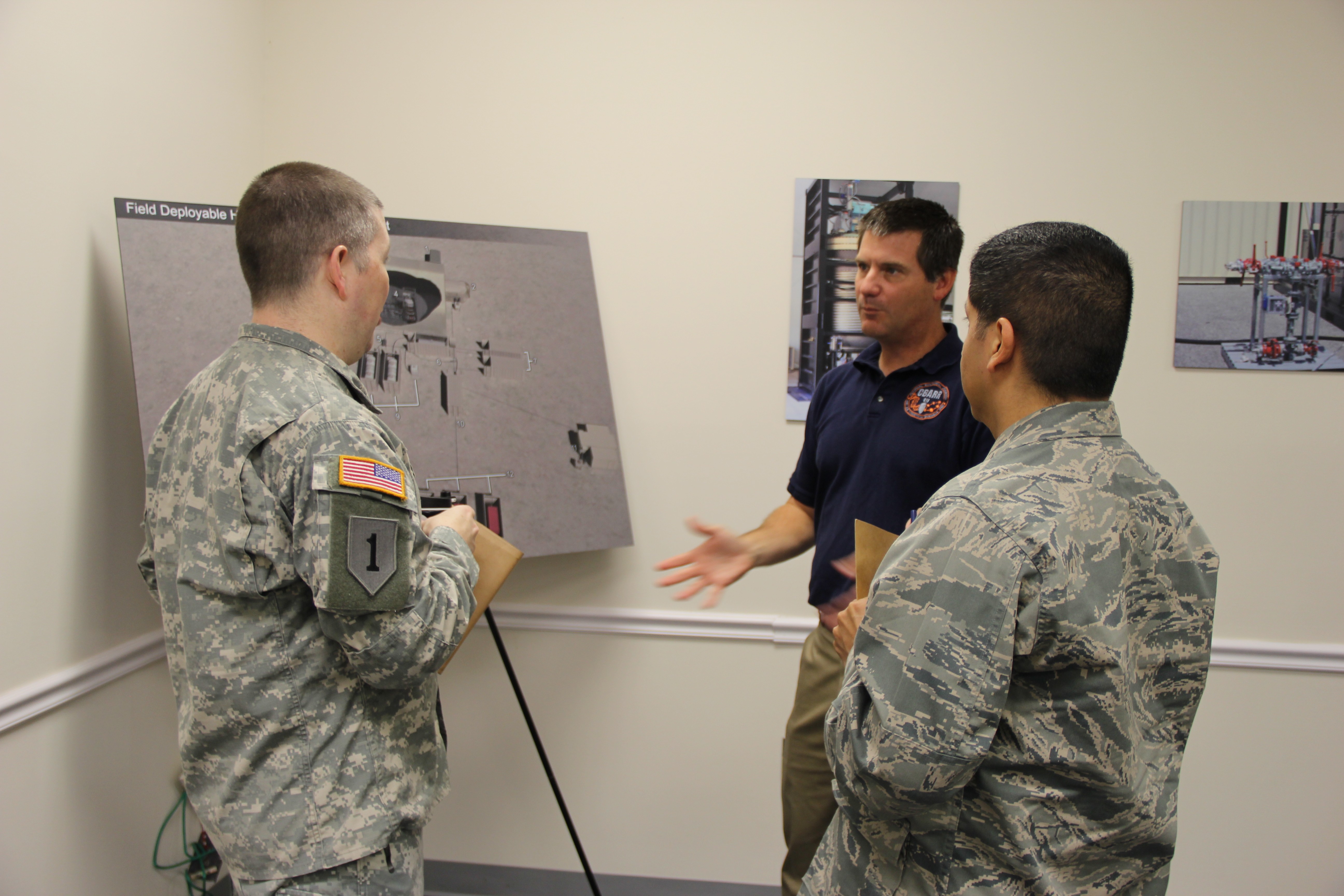
Department of Defense stakeholders across numerous organizations attended the demonstration, which included an information session about the technology and a walk-through of the simulated project site, including support equipment, mobile laboratory and personnel decontamination station. Resident subject matter experts engaged with stakeholders during the tour and answered questions regarding the components, design, functionality and overview of the entire system. ECBC, DTRA, JPEO-CBD, the U.S. Army Chemical Materials Activity and the U.S. Army Contracting Command are responsible for the design, procurement, fabrication, testing and training of the FDHS.
"The team that worked on this project has delivered a beginning-to-end solution for a complex problem," said Blades. "Every organization came together and brought their expertise to the table. It's been a team effort from the start, and it's nice to see it transition for further development."
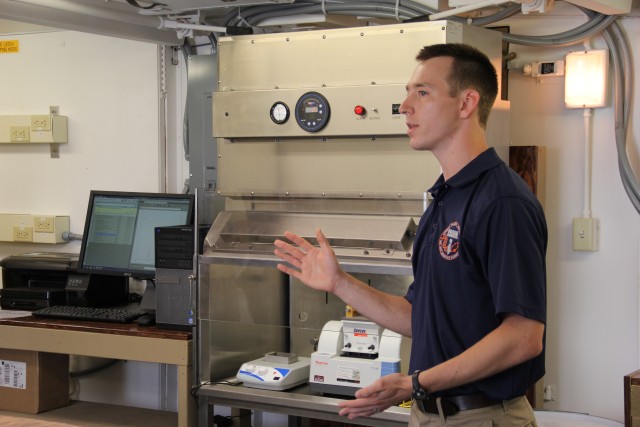
ECBC's rapid prototyping capabilities and field operational experience were vital to the design and functionality of the FDHS. Engineers and technicians discussed various design plans and blueprints, and screened and analyzed more than 40 technologies throughout the process. This technical expertise was combined with CMA's experience in building and operating chemical agent neutralization facilities like those located at Aberdeen Proving Ground and Newport Chemical Depot in Indiana, and Pine Bluff Arsenal in Arkansas. Those facilities have safely and successfully completed their chemical agent disposal missions.
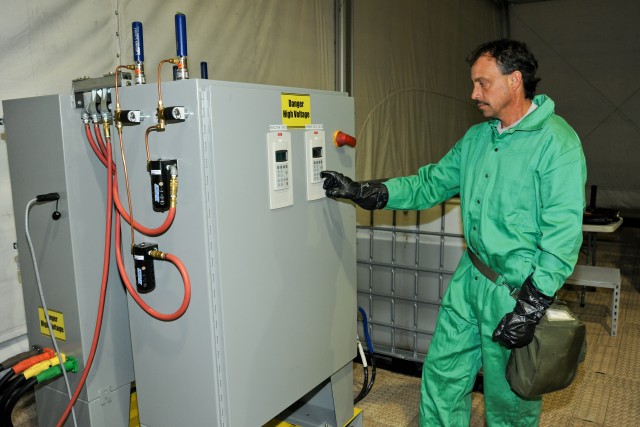
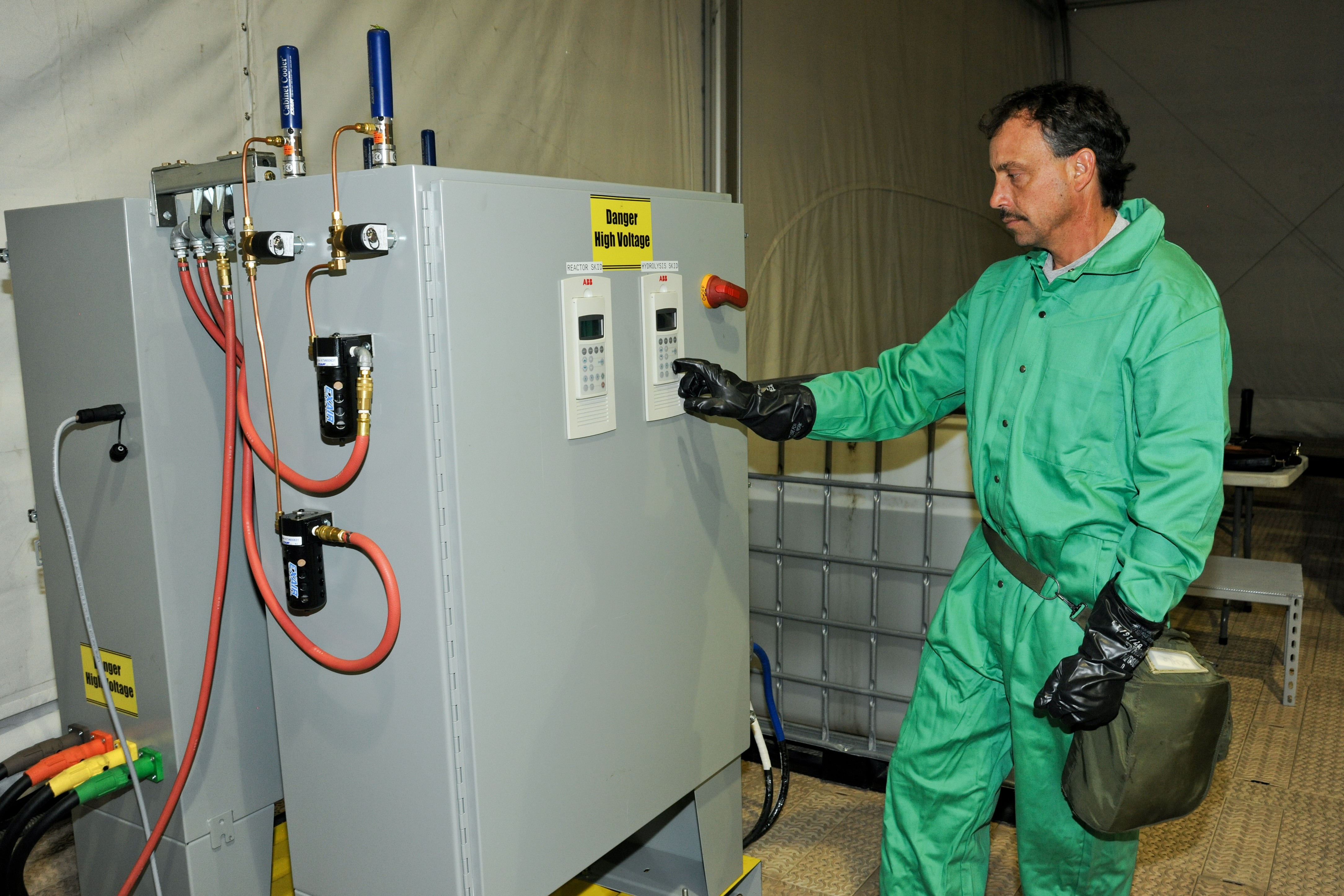
Once onsite, a crew of 15 personnel is needed each shift for 24/7 operational capability. The full FDHS site includes power generators and a laboratory that is fully capable out of the box, needing only consumable materials such as water, reagents and fuel to operate. The FDHS is also equipped with redundant critical systems that ensure maximum reliability. Throughput varies from five to 25 metric tons per day, depending on the material being treated. To increase throughput rates, multiple units can be co-located onsite, which also enables the sharing of security and other assets.
================================
ECBC is part of the U.S. Army Research, Development and Engineering Command, which has the mission to develop technology and engineering solutions for America's Soldiers.
RDECOM is a major subordinate command of the U.S. Army Materiel Command. AMC is the Army's premier provider of materiel readiness -- technology, acquisition support, materiel development, logistics power projection, and sustainment -- to the total force, across the spectrum of joint military operations. If a Soldier shoots it, drives it, flies it, wears it, eats it or communicates with it, AMC provides it.
Related Links:
U.S. Army Research, Development and Engineering Command
U.S. Army Chemical Materials Activity
Defense Threat Reduction Agency
U.S. Army Edgewood Chemical Biological Center
Joint Program Executive Office for Chemical and Biological Defense





















Social Sharing